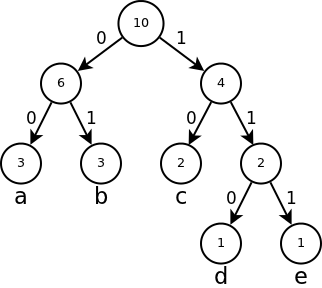
二元樹(Binary tree)
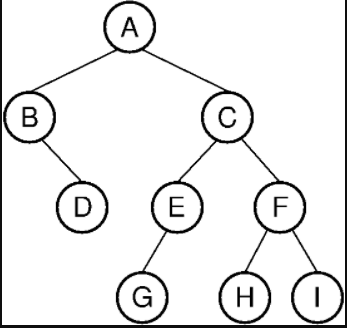
樹狀結構的定義
樹(tree)是一種特殊的資料結構,它可以用來描述有分支的結構,是由一個或一個以上的節點所組成的有限集合, 且具有下列特質:
- 存在一個特殊的節點,稱為樹根( root)。
- 其餘的節點分為n ≥ 0 個互斥的集合,T1, T2, T3…Tn,且每個集合稱為子樹。
樹狀結構的名詞
- 父節點(parent):每一個節點的上層節點為父節點 。
- 子節點(children):每一個節點的下層節點為子節點。
- 兄弟節點(siblings):有共同父節點的節點為兄弟節點。
- 分支度(degree):子樹的個數為該節點的分支度。
- 終端節點或樹葉節點(terminal node):沒有子節點的節點。
- 非終端節點(non-terminal node):樹葉以外的節點均為非終端節點。
二元樹的定義
二元樹是每個節點最多只有兩個分支的樹結構。通常分支被稱作「左子樹」和「右子樹」。二元樹的分支具有左右次序,不能顛倒。
二元樹通常作為資料結構應用,典型用法是對節點定義一個標記函式,將一些值與每個節點相關聯。這樣標記的二元樹就可以實現二元搜尋樹和二元堆積,並應用於高效率的搜尋和排序。
interface BinNode { // Binary tree node ADT
// Get and set the element value
Object element();
void setElement(Object v);
// return the children
BinNode left();
BinNode right();
// return TRUE if a leaf node, FALSE otherwise
boolean isLeaf();
}
節點數
二元樹的第i層至多擁有 個節點數;深度為 k的二元樹至多總共有 個節點數。對任何一棵非空的二元樹T,如果其葉片(終端節點)數為n0,分支度為2的節點數為n2,則n0 = n2 + 1。
特殊的二元樹
- 滿二元樹(full binary tree) :除了樹葉以外,每個節點都有兩個小孩。
- 完全二元樹(complete binary tree) :各層節點全滿,除了最後一層,最後一層節點全部靠左。
二元樹的走訪(Binary Tree Traversal)
中序走訪(Inorder traversal)
void inorder(BinNode rt) {
if (rt == null) return; // Empty subtree - do nothing
preorder(rt.left()); /* 走訪左子樹 */
visit(rt); /* 走訪列印樹根 */
preorder(rt.right()); /* 走訪右子樹 */
}
前序走訪(Preorder traversal)
void preorder(BinNode rt) {
if (rt == null) return; // Empty subtree - do nothing
visit(rt); /* 走訪列印樹根 */
preorder(rt.left()); /* 走訪左子樹 */
preorder(rt.right()); /* 走訪右子樹 */
}
後序走訪(Postorder traversal)
void postorder(BinNode rt) {
if (rt == null) return; // Empty subtree - do nothing
preorder(rt.left()); /* 走訪左子樹 */
preorder(rt.right()); /* 走訪右子樹 */
visit(rt); /* 走訪列印樹根 */
}
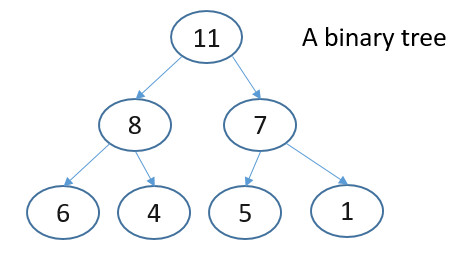
C版本的中序/前序/後序走訪
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int value;
struct node *childLeft;
struct node *childRight;
};
struct node * InitTree()
{
struct node *root;
struct node *child;
//11
root = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
root->value = 11;
root->childLeft = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
root->childRight = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
//8
child = root->childLeft;
child->value = 8;
child->childLeft = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
child->childRight = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
//7
child = root->childRight;
child->value = 7;
child->childLeft = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
child->childRight = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
//6
child = root->childLeft->childLeft;
child->value = 6;
child->childLeft = NULL;
child->childRight = NULL;
//4
child = root->childLeft->childRight;
child->value = 4;
child->childLeft = NULL;
child->childRight = NULL;
//5
child = root->childRight->childLeft;
child->value = 5;
child->childLeft = NULL;
child->childRight = NULL;
//1
child = root->childRight->childRight;
child->value = 1;
child->childLeft = NULL;
child->childRight = NULL;
return root;
}
void PrintPreOrder(struct node *root)
{
//Pre-order
if (root !=NULL)
printf("%d->", root->value);
if (root->childLeft!= NULL)
PrintPreOrder(root->childLeft);
if (root->childRight!= NULL)
PrintPreOrder(root->childRight);
}
void PrintInOrder(struct node *root)
{
//In-order
if (root->childLeft!= NULL)
PrintInOrder(root->childLeft);
if (root !=NULL)
printf("%d->", root->value);
if (root->childRight!= NULL)
PrintInOrder(root->childRight);
}
void PrintPostOrder(struct node *root)
{
//Post-order
if (root->childLeft!= NULL)
PrintPostOrder(root->childLeft);
if (root->childRight!= NULL)
PrintPostOrder(root->childRight);
if (root !=NULL)
printf("%d->", root->value);
}
int main()
{
struct node *root = InitTree();
printf("\nPre-order :");PrintPreOrder(root);
printf("\nIn-order :");PrintInOrder(root);
printf("\nPost-order:");PrintPostOrder(root);
}
//output:
//Pre-order :11->8->6->4->7->5->1->
//In-order :6->8->4->11->5->7->1->
//Post-order:6->4->8->5->1->7->11->
java版本的中序/前序/後序走訪
class Node {
public int value=0;
public Node childLeft=null;
public Node childRight=null;
}
public class Ex2Class {
static Node InitTree() {
//11
Node root = new Node();
root.value = 11;
root.childLeft = new Node();
root.childRight = new Node();
//8
Node child = root.childLeft;
child.value = 8;
child.childLeft = new Node();
child.childRight = new Node();
//7
child = root.childRight;
child.value = 7;
child.childLeft = new Node();
child.childRight = new Node();
//6
child = root.childLeft.childLeft;
child.value = 6;
//4
child = root.childLeft.childRight;
child.value = 4;
//5
child = root.childRight.childLeft;
child.value = 5;
//1
child = root.childRight.childRight;
child.value = 1;
return root;
}
static void PrintPreOrder(Node root){
//Pre-order
if (root != null){
System.out.printf("%d->", root.value);
}
if (root.childLeft!= null){
PrintPreOrder(root.childLeft);
}
if (root.childRight!= null){
PrintPreOrder(root.childRight);
}
}
static void PrintInOrder(Node root){
//In-order
if (root.childLeft!= null){
PrintInOrder(root.childLeft);
}
if (root != null){
System.out.printf("%d->", root.value);
}
if (root.childRight!= null){
PrintInOrder(root.childRight);
}
}
static void PrintPostOrder(Node root){
//Post-order
if (root.childLeft!= null){
PrintPostOrder(root.childLeft);
}
if (root.childRight!= null){
PrintPostOrder(root.childRight);
}
if (root != null){
System.out.printf("%d->", root.value);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = InitTree();
System.out.printf("\nPre-order :");
PrintPreOrder(root);
System.out.printf("\nIn-order :");
PrintInOrder(root);
System.out.printf("\nPost-order:");
PrintPostOrder(root);
}
}
Go版本的中序/前序/後序走訪
package main
import "fmt"
type Node struct {
value int
childLeft *Node
childRight *Node
}
func InitTree() Node{
//11
root := Node{}
root.value = 11
root.childLeft = &Node{}
root.childRight = &Node{}
//8
child := root.childLeft;
child.value = 8;
child.childLeft = &Node{}
child.childRight = &Node{}
//7
child = root.childRight;
child.value = 7;
child.childLeft = &Node{}
child.childRight = &Node{}
//6
child = root.childLeft.childLeft;
child.value = 6;
//4
child = root.childLeft.childRight;
child.value = 4;
//5
child = root.childRight.childLeft;
child.value = 5;
//1
child = root.childRight.childRight;
child.value = 1;
return root
}
func PrintPreOrder(root *Node){
//Pre-order
if (root != nil){
fmt.Printf("%d->", root.value)
}
if (root.childLeft!= nil){
PrintPreOrder(root.childLeft)
}
if (root.childRight!= nil){
PrintPreOrder(root.childRight)
}
}
func PrintInOrder(root *Node){
//In-order
if (root.childLeft!= nil){
PrintInOrder(root.childLeft)
}
if (root !=nil){
fmt.Printf("%d->", root.value)
}
if (root.childRight!= nil){
PrintInOrder(root.childRight)
}
}
func PrintPostOrder(root *Node){
//Post-order
if (root.childLeft!= nil){
PrintPostOrder(root.childLeft)
}
if (root.childRight!= nil){
PrintPostOrder(root.childRight)
}
if (root != nil){
fmt.Printf("%d->", root.value)
}
}
func main() {
root := InitTree()
fmt.Print("\nPre-order :")
PrintPreOrder(&root)
fmt.Print("\nIn-order :")
PrintInOrder(&root)
fmt.Print("\nPost-order:")
PrintPostOrder(&root)
}
二元搜尋樹Binary Search Tree
二元搜尋樹是指一棵空樹或者具有下列性質的二元樹:
- 若任意節點的左子樹不空,則左子樹上所有節點的值均小於它的根節點的值;
- 若任意節點的右子樹不空,則右子樹上所有節點的值均大於它的根節點的值;
- 任意節點的左、右子樹也分別為二元搜尋樹;
- 沒有鍵值相等的節點。 二元搜尋樹相比於其他資料結構的優勢在於搜尋、插入的時間複雜度較低。為。二元搜尋樹是基礎性資料結構,用於構建更為抽象的資料結構,如集合、multiset、關聯數組等。
// Binary Search Tree implementation
class BST {
private BSTNode root; // Root of the BST
private int nodecount; // Number of nodes in the BST
// constructor
BST() { root = null; nodecount = 0; }
// Reinitialize tree
void clear() { root = null; nodecount = 0; }
// Insert a record into the tree.
// Records can be anything, but they must be Comparable
// e: The record to insert.
void insert(Comparable e) {
root = inserthelp(root, e);
nodecount++;
}
// Remove a record from the tree
// k: The key value of record to remove
// Returns the record removed, null if there is none.
Comparable remove(Comparable k) {
Comparable temp = findhelp(root, k); // First find it
if (temp != null) {
root = removehelp(root, k); // Now remove it
nodecount--;
}
return temp;
}
// Return the record with key value k, null if none exists
// k: The key value to find
Comparable find(Comparable k) { return findhelp(root, k); }
// Return the number of records in the dictionary
int size() { return nodecount; }
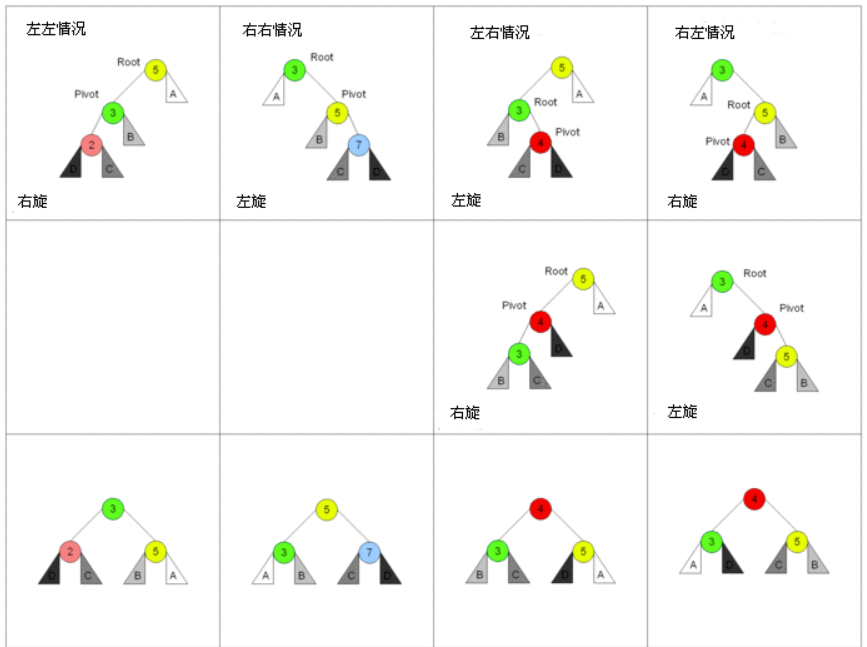
平衡樹AVL Tree
在AVL樹中任何節點的兩個子樹的高度最大差別為1。
AVL旋轉
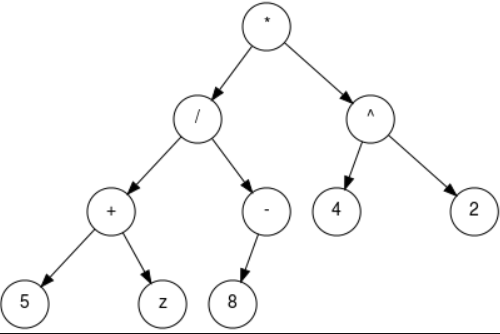
二元運算樹(Binary Expression Tree)
((5 + z) / -8) * (4 ^ 2)
Heap堆積
堆積通常是一個可以被看做一棵樹的陣列物件。在佇列中,排程程式反覆提取佇列中第一個作業並執行,因為實際情況中某些時間較短的任務將等待很長時間才能結束,或者某些不短小,但具有重要性的作業,同樣應當具有優先權。堆積即為解決此類問題設計的一種資料結構。
- 最大堆積(Max Heap) 是一個完全二元樹(Complete binary tree) ,且其特性是每個子樹(subtree) 的根節點(root node) 的值一定比該子樹其他節點的值還大。
- 最小堆積(Min Heap) 是一個完全二元樹(Complete binary tree) ,且其特性是每個子樹(subtree) 的根節點(root node) 的值一定比該子樹其他節點的值還小。 *最小-最大堆積(Min-Max Heap)是一個完整二元樹。此二元樹是交替的階層方式呈現,分別為最小階層 ( min level ) 和最大階層 ( max level ) ,這裡實作樹根為最大鍵值。
// Max-heap implementation
class MaxHeap {
private Comparable[] Heap; // Pointer to the heap array
private int size; // Maximum size of the heap
private int n; // Number of things now in heap
// Constructor supporting preloading of heap contents
MaxHeap(Comparable[] h, int num, int max)
{ Heap = h; n = num; size = max; buildheap(); }
// Return current size of the heap
int heapsize() { return n; }
// Return true if pos a leaf position, false otherwise
boolean isLeaf(int pos)
{ return (pos >= n/2) && (pos < n); }
// Return position for left child of pos
int leftchild(int pos) {
if (pos >= n/2) return -1;
return 2*pos + 1;
}
// Return position for right child of pos
int rightchild(int pos) {
if (pos >= (n-1)/2) return -1;
return 2*pos + 2;
}
// Return position for parent
int parent(int pos) {
if (pos <= 0) return -1;
return (pos-1)/2;
}
// Insert val into heap
void insert(int key) {
if (n >= size) {
println("Heap is full");
return;
}
int curr = n++;
Heap[curr] = key; // Start at end of heap
// Now sift up until curr's parent's key > curr's key
while ((curr != 0) && (Heap[curr].compareTo(Heap[parent(curr)]) > 0)) {
swap(Heap, curr, parent(curr));
curr = parent(curr);
}
}
// Heapify contents of Heap
void buildheap()
{ for (int i=n/2-1; i>=0; i--) siftdown(i); }
// Put element in its correct place
void siftdown(int pos) {
if ((pos < 0) || (pos >= n)) return; // Illegal position
while (!isLeaf(pos)) {
int j = leftchild(pos);
if ((j<(n-1)) && (Heap[j].compareTo(Heap[j+1]) < 0))
j++; // j is now index of child with greater value
if (Heap[pos].compareTo(Heap[j]) >= 0) return;
swap(Heap, pos, j);
pos = j; // Move down
}
}
// Remove and return maximum value
Comparable removemax() {
if (n == 0) return -1; // Removing from empty heap
swap(Heap, 0, --n); // Swap maximum with last value
if (n != 0) // Not on last element
siftdown(0); // Put new heap root val in correct place
return Heap[n];
}
// Remove and return element at specified position
Comparable remove(int pos) {
if ((pos < 0) || (pos >= n)) return -1; // Illegal heap position
if (pos == (n-1)) n--; // Last element, no work to be done
else {
swap(Heap, pos, --n); // Swap with last value
// If we just swapped in a big value, push it up
while ((pos > 0) && (Heap[pos].compareTo(Heap[parent(pos)]) > 0)) {
swap(Heap, pos, parent(pos));
pos = parent(pos);
}
if (n != 0) siftdown(pos); // If it is little, push down
}
return Heap[n];
}
}
霍夫曼編碼樹(Huffman Coding Tree)