Java語言復習
使用 Eclipse 寫 Java 程式
Step1
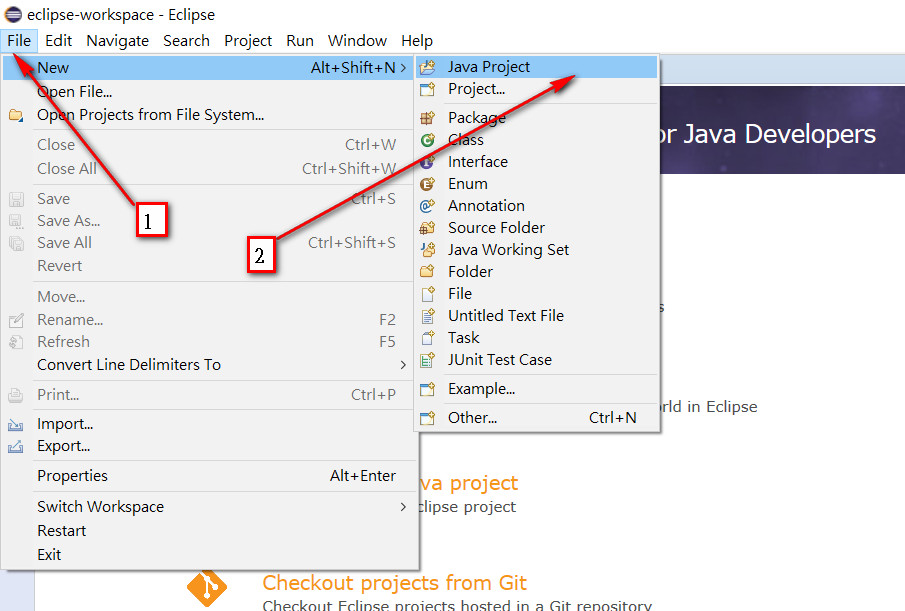
Step2
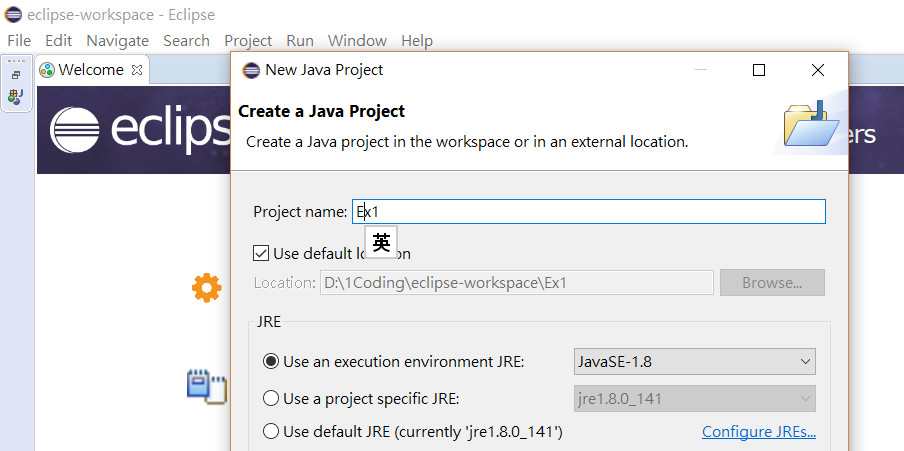
Step3
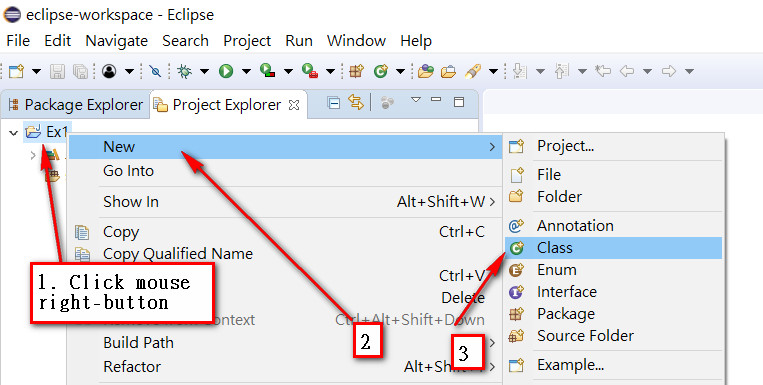
Step4
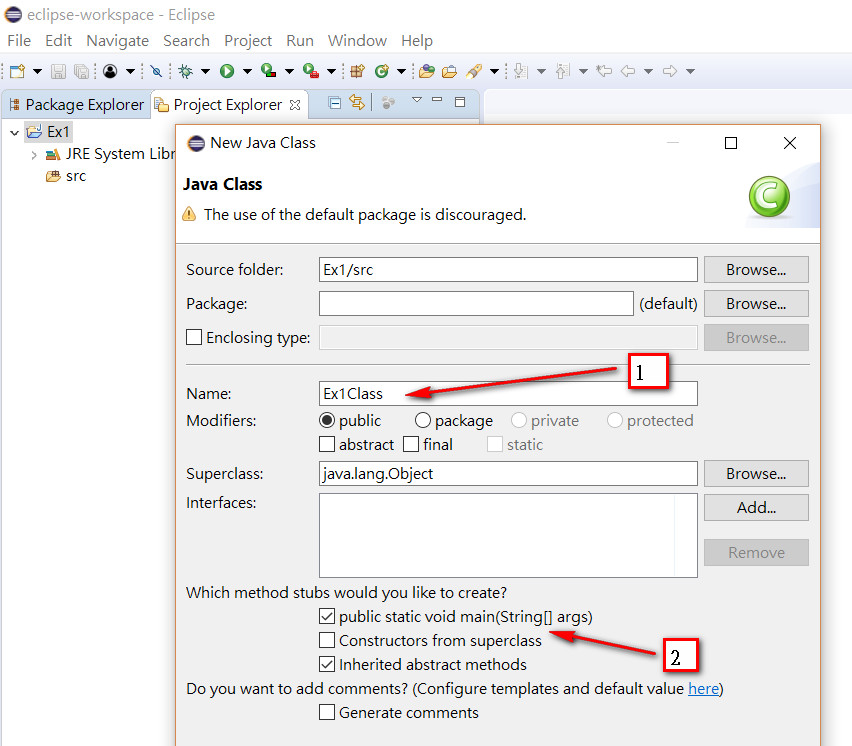
Java語言的Hello world程式
public class Ex1Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
}
說明
Java程式的組成
寫程式基本上就是由輸入資料經過運算然後得到輸出。這樣的過程可以簡化成五個部份:一、宣告變數。二、進行運算。三、控制流程。四、判斷資料的值。五、輸入及輸出。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex2Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.printf("Input ID:");
int nID = sc.nextInt();
int even = 0, odd = 0, digits=0;
int num=nID;
while (num >0){
digits++;
if (num%2==0)
even++;
num /=10;
}
odd = digits - even;
System.out.printf("My ID: %9d -- %d digits %d odd nums %d even nums\n", nID, digits, odd, even);
}
}
說明
Java Loop
String [] a = {"1","3","5","7","9","11"};
//5.0前的for迴圈寫法
for(int i = 0 ; i < a.length ; i++){
String temp = a[i];
System.out.print(temp + ", ");
}
//5.0後for迴圈也可以用這種新的寫法(for-each)
for(String temp : a){
System.out.print(temp + ", ");
}
表示式及指定式
| 運算子的種類 | 優先順序 |
|---|---|
| ( ) | 8 |
| -- ++ ! & | 7 |
| * / % | 6 |
| + - | 5 |
| > < >= <= | 4 |
| == != | 3 |
| && | 2 |
| || | 1 |
從命令列輸入值
double d1, d2;
int a1, a2;
d1 = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
d2 = Double.parseDouble(args[1]);
a1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
a2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
從檔案輸入
try
{
//In
FileReader reader = new FileReader("math.txt");
BufferedReader sr = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = sr.readLine();
while (line != null && line.length() > 0)
{
int score = Integer.parseInt(line);
line = sr.readLine();
}
sr.close();
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fe)
{
System.out.printf(fe.getMessage());
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
System.out.printf(ie.getMessage());
}
從檔案輸出
try
{
//Out
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(result.txt);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(writer);
System.out.printf("%2d => %5.2f\n", score, modified);
pw.printf("%5.2f", modified);pw.println();
pw.close();
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fe)
{
System.out.printf(fe.getMessage());
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
System.out.printf(ie.getMessage());
}
產生亂數
Random random = new Random();
int num= (random.nextInt()& Integer.MAX_VALUE)%1000+1001;
把字串切開
String[] numStr = line.split(" ");
Java.util.ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an empty array list with an initial capacity
ArrayList<Integer> arrlist = new ArrayList<Integer>(5);
// use add() method to add elements in the deque
arrlist.add(20);
arrlist.add(15);
arrlist.add(30);
arrlist.add(45);
System.out.println("Size of list: " + arrlist.size());
// let us print all the elements available in list
for (Integer number : arrlist) {
System.out.println("Number = " + number);
}
// Removes element at 3rd position
arrlist.remove(2);
System.out.println("Now, Size of list: " + arrlist.size());
// let us print all the elements available in list
for (Integer number : arrlist) {
System.out.println("Number = " + number);
}
}
}
Java.util.LinkedList
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a LinkedList
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
// add some elements
list.add("Hello");
list.add(2);
list.add("Chocolate");
list.add("10");
// print the list
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
// remove the element at index 2
System.out.println("Element to be removed:" + list.remove(2));
// print the list
System.out.println("LinkedList:" + list);
}
}