Go語言摘要
Go home https://golang.org/
Go tutorial https://tour.golang.org/welcome/1
下載Go, 用Visual studio code 寫 Go 程式
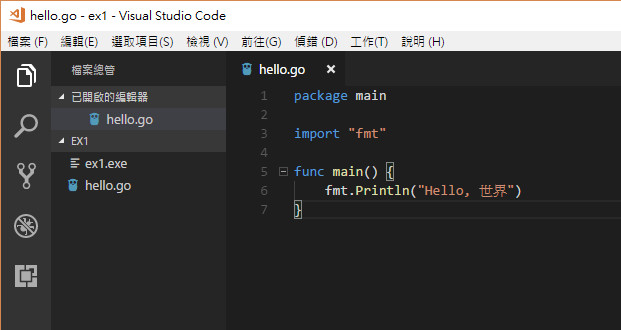
Go語言的Hello world程式
go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello world")
}
和java比較
package main;
import java.io.*;
public class Ex1Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
}
說明
- Go程式的由Packages(套件)組成。第一行package main表示這是一個可以啟動執行main()函數的程式
- Go程式的statements(敘述)可以加 ";", 也可以不加
Go程式的組成
寫程式基本上就是由輸入資料經過運算然後得到輸出。這樣的過程可以簡化成五個部份:一、宣告變數。二、進行運算。三、控制流程。四、判斷資料的值。五、輸入及輸出。
一、宣告變數
var i int
var U, V, W float64
var k = 0
var x, y float32 = -1, -2
var (
i int
u, v, s = 2.0, 3.0, "bar"
)
//Short variable declarations
i, j := 0, 10
f := func() int { return 7 }
二、進行運算
r = z; r += x*y
t = x*y; r = t + z
三、控制流程
//普通三條件迴圈
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
f(i)
}
//等於其他程式語言的while
for a < b {
a *= 2
}
//range 等於其他語言的foreach
var a [10]string
for i, s := range a {
// type of i is int
// type of s is string
// s == a[i]
g(i, s)
}
kvs := map[string]string{"a": "apple", "b": "banana"}
for k, v := range kvs {
fmt.Printf("%s -> %s\n", k, v)
}
四、判斷資料的值
//單一條件的if
if x > max {
x = max
}
//if-else
if x := f(); x < y {
return x
} else if x > z {
return z
} else {
return y
}
//switch
switch tag {
default: s3()
case 0, 1, 2, 3: s1()
case 4, 5, 6, 7: s2()
}
switch x := f(); { // missing switch expression means "true"
case x < 0: return -x
default: return x
}
switch {
case x < y: f1()
case x < z: f2()
case x == 4: f3()
}
五、輸入及輸出
package main
import "os"
inFile, _ := os.Open(path)
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(inFile)
scanner.Split(bufio.ScanLines)
for scanner.Scan() {
fmt.Println(scanner.Text())
}
函數多重返回值
go
package main
import "fmt"
func swap(x, y string) (string, string) {
return y, x
}
func split(sum int) (x, y int) {
x = sum * 4 / 9
y = sum - x
return
}
func main() {
a, b := swap("hello", "world")
fmt.Println(a, b)
//
fmt.Println(split(17))
}
說明
- a, b := swap("hello", "world") swap()有兩個輸入參數和兩個返回值
- x, y int是有命名的返回值
Go語言的特點:defer, go, select
defer
A "defer" statement invokes a function whose execution is deferred to the moment the surrounding function returns.
func readLine(path string) {
//開啟檔案
inFile, _ := os.Open(path)
//
defer inFile.Close()
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(inFile)
scanner.Split(bufio.ScanLines)
for scanner.Scan() {
fmt.Println(scanner.Text())
}
}
Go
A "go" statement starts the execution of a function call as an independent concurrent thread of control, or goroutine, within the same address space.
go Server()
go func(ch chan<- bool) { for { sleep(10); ch <- true }} (c)
Select
A "select" statement chooses which of a set of possible send or receive operations will proceed. It looks similar to a "switch" statement but with the cases all referring to communication operations.
var a []int
var c, c1, c2, c3, c4 chan int
var i1, i2 int
select {
case i1 = <-c1:
print("received ", i1, " from c1\n")
case c2 <- i2:
print("sent ", i2, " to c2\n")
case i3, ok := (<-c3): // same as: i3, ok := <-c3
if ok {
print("received ", i3, " from c3\n")
} else {
print("c3 is closed\n")
}
case a[f()] = <-c4:
// same as:
// case t := <-c4
// a[f()] = t
default:
print("no communication\n")
}
for { // send random sequence of bits to c
select {
case c <- 0: // note: no statement, no fallthrough, no folding of cases
case c <- 1:
}
}
select {} // block forever
從命令列輸入值
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1, d2;
int a1, a2;
d1 = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
d2 = Double.parseDouble(args[1]);
a1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
a2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
}
go
package main
import "os"
import "fmt"
func main() {
argsWithProg := os.Args
argsWithoutProg := os.Args[1:]
arg := os.Args[3]
fmt.Println(argsWithProg)
fmt.Println(argsWithoutProg)
fmt.Println(arg)
}
從檔案輸入
java
try
{
//In
FileReader reader = new FileReader("math.txt");
BufferedReader sr = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = sr.readLine();
while (line != null && line.length() > 0)
{
int score = Integer.parseInt(line);
line = sr.readLine();
}
sr.close();
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fe)
{
System.out.printf(fe.getMessage());
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
System.out.printf(ie.getMessage());
}
go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println(argsWithProg)
fmt.Println(argsWithoutProg)
fmt.Println(arg)
}
從檔案輸出
java
try
{
//Out
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(result.txt);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(writer);
System.out.printf("%2d => %5.2f\n", score, modified);
pw.printf("%5.2f", modified);pw.println();
pw.close();
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fe)
{
System.out.printf(fe.getMessage());
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
System.out.printf(ie.getMessage());
}
產生亂數
java
Random rnd = new Random();
int[] ball = new int[49];//int ball[49];
for (int k = 0; k < 49; k++)
{
ball[k] = rnd.nextInt();;
}
go
package main
import "fmt"
import "math/rand"
import "time"
import "strconv"
func main() {
//int i;
s1 := rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano())
rand1 := rand.New(s1)
for i:=0; i<10; i++ {
val := rand1.Intn(2000)
fmt.Println("Number "+strconv.Itoa(val))
}
}
把字串切開
java
String[] numStr = line.split(" ");
go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
s := strings.Split("127.0.0.1:5432", ":")
ip, port := s[0], s[1]
fmt.Println(ip, port)
}
Go Package list
https://golang.org/pkg/container/list/
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
// Create a new list and put some numbers in it.
l := list.New()
e4 := l.PushBack(4)
e1 := l.PushFront(1)
l.InsertBefore(3, e4)
l.InsertAfter(2, e1)
// Iterate through list and print its contents.
for e := l.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
fmt.Println(e.Value)
}
}