排序
排序演算法(Sorting algorithm)是一種能將一串資料依照特定排序方式進行排列的一種演算法。
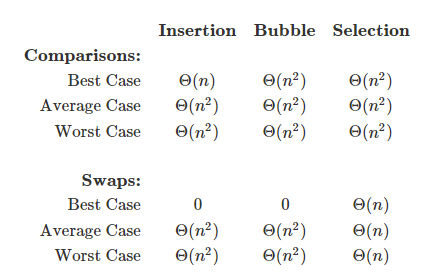
- 計算的時間複雜度(最差、平均、和最好表現)。一般而言,好的表現是,且壞的表現是。對於一個排序理想的表現是。平均上總是至少需要 。
- 記憶體使用量
- 穩定性(stability):穩定排序演算法會讓原本有相等鍵值的紀錄維持相對次序。也就是如果一個排序演算法是穩定的,當有兩個相等鍵值的紀錄R和S,且在原本的串列中R出現在S之前,在排序過的串列中R也將會是在S之前。
常見排序演算法種類
簡單排序(Simple sorts)
- Insertion sort
- Selection sort
- Bubble sort
高效排序(Efficient sorts)
- Merge sort
- Heapsort
- Quicksort
- Bubble sort and variants
分散排序(Distribution sort)
- Counting sort
- Bucket sort
- Radix sort
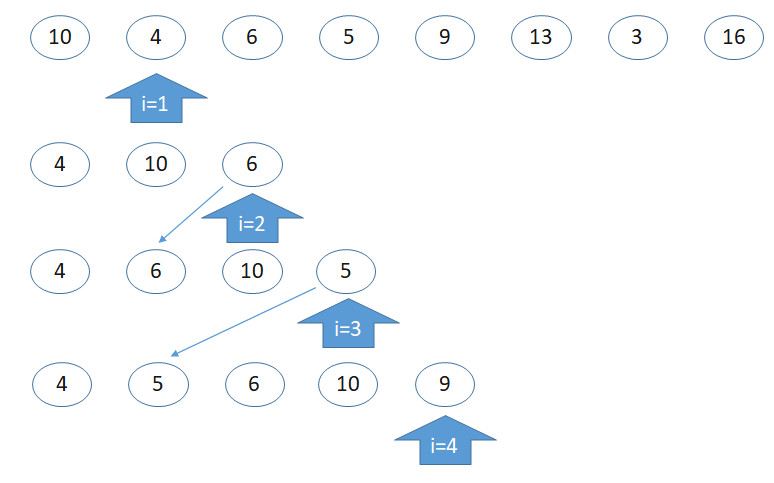
插入排序(insertion sort)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insertion_sort
void insertion_sort(int arr[], int len)
{
int i,j,temp;
for (i = 1 ; i < len ; i++ ){
temp = arr[i];
for (j = i; j > 0 && arr[j-1] > temp ; j--){
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
氣泡排序(bubble sort)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bubble_sort
void bubble_sort(int arr[], int len) {
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++){
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}

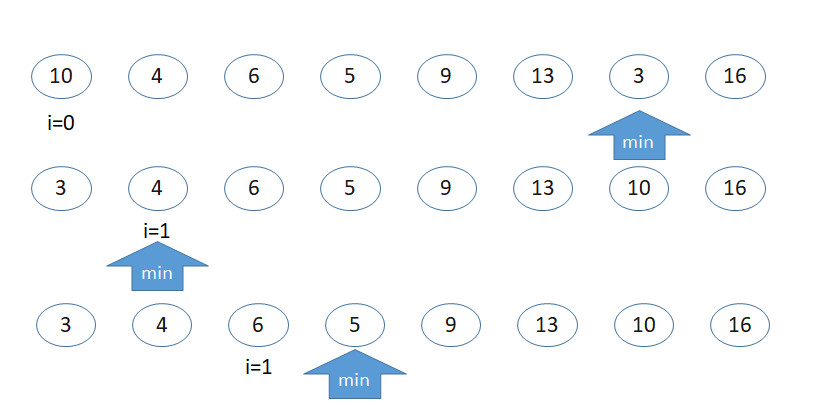
選擇排序(selection sort)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selection_sort
void swap(int *a,int *b) //交換兩個變數
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void selection_sort(int arr[], int len)
{
int i,j;
for (i = 0 ; i < len - 1 ; i++){
int min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++){ //走訪未排序的元素
if (arr[j] < arr[min]){ //找到目前最小值
min = j; //紀錄最小值
}
}
swap(&arr[min], &arr[i]); //做交換
}
}
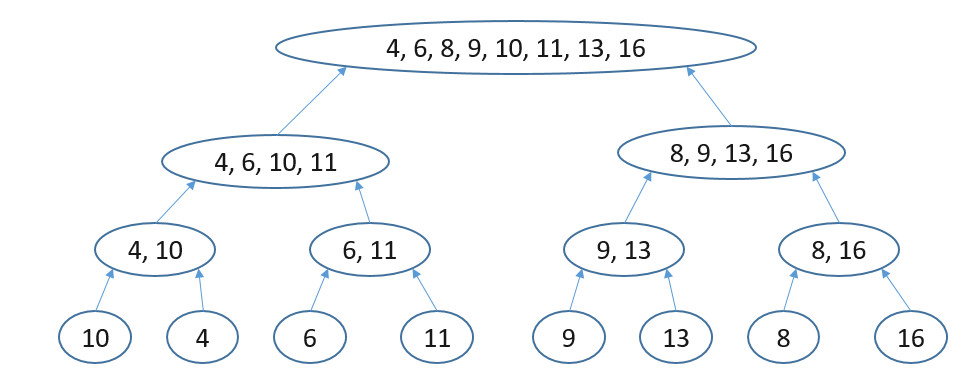
合併排序(merge sort)
import java.util.*;
public class MergerSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Unsorted array
Integer[] a = { 2, 6, 3, 5, 1 };
//Call merge sort
mergeSort(a);
//Check the output which is sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public static Comparable[] mergeSort(Comparable[] list)
{
//If list is empty; no need to do anything
if (list.length <= 1) {
return list;
}
//Split the array in half in two parts
Comparable[] first = new Comparable[list.length / 2];
Comparable[] second = new Comparable[list.length - first.length];
System.arraycopy(list, 0, first, 0, first.length);
System.arraycopy(list, first.length, second, 0, second.length);
//Sort each half recursively
mergeSort(first);
mergeSort(second);
//Merge both halves together, overwriting to original array
merge(first, second, list);
return list;
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
private static void merge(Comparable[] first, Comparable[] second, Comparable[] result)
{
//Index Position in first array - starting with first element
int iFirst = 0;
//Index Position in second array - starting with first element
int iSecond = 0;
//Index Position in merged array - starting with first position
int iMerged = 0;
//Compare elements at iFirst and iSecond,
//and move smaller element at iMerged
while (iFirst < first.length && iSecond < second.length)
{
if (first[iFirst].compareTo(second[iSecond]) < 0)
{
result[iMerged] = first[iFirst];
iFirst++;
}
else
{
result[iMerged] = second[iSecond];
iSecond++;
}
iMerged++;
}
//copy remaining elements from both halves - each half will have already sorted elements
System.arraycopy(first, iFirst, result, iMerged, first.length - iFirst);
System.arraycopy(second, iSecond, result, iMerged, second.length - iSecond);
}
}
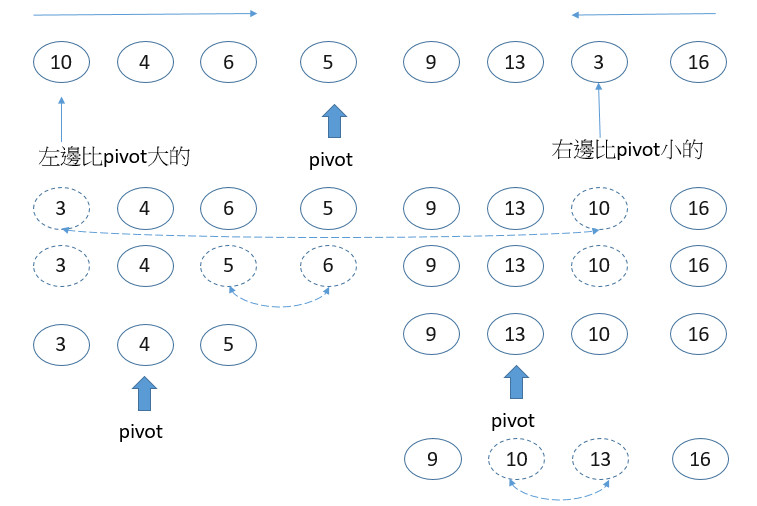
快速排序(quick sort)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort 快速排序使用分治法(Divide and conquer)策略來把一個序列(list)分為兩個子序列(sub-lists)。 步驟為: 從數列中挑出一個元素,稱為"基準"(pivot), 重新排序數列,所有比基準值小的元素擺放在基準前面,所有比基準值大的元素擺在基準後面(相同的數可以到任何一邊)。在這個分割結束之後,該基準就處於數列的中間位置。這個稱為分割(partition)操作。 遞迴地(recursively)把小於基準值元素的子數列和大於基準值元素的子數列排序。
void quicksort(Comparable* A[], int i, int j) {
int pivotindex = findpivot(i, j);
swap(A, pivotindex, j); // Stick pivot at end
// k will be the first position in the right subarray
int k = partition(A, i, j-1,A[j]);
swap(A, k, j); // Put pivot in place
if ((k-i) > 1) quicksort(A, i, k-1); // Sort left partition
if ((j-k) > 1) quicksort(A, k+1, j); // Sort right partition
}
int partition(Comparable* A[], int left, int right, Comparable* pivot) {
while (left <= right) { // Move bounds inward until they meet
while (*A[left] < *pivot) left++;
while ((right >= left) && (*A[right] >= *pivot)) right--;
if (right > left) swap(A, left, right); // Swap out-of-place values
}
return left; // Return first position in right partition
}
堆積排序(heap sort)
static <E extends Comparable<? super E>>
void heapsort(E[] A) {
// The heap constructor invokes the buildheap method
MaxHeap<E> H = new MaxHeap<E>(A, A.length, A.length);
for (int i=0; i<A.length; i++) // Now sort
H.removemax(); // Removemax places max at end of heap
}
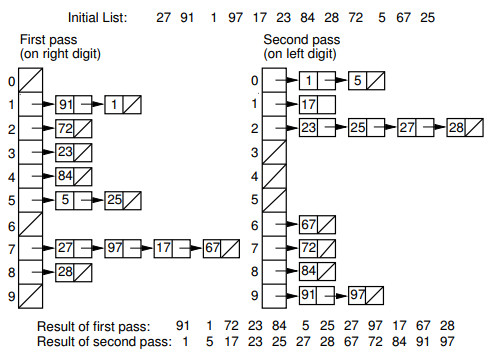
基數排序(radix sort)
static void radixsort(int A[], int k, int r, int n) {
int B[n];
int count[r];
int i, j, rtok;
for (i = 0, rtok = 1; i < k; i++, rtok *= r) { // For k digits
for (j = 0; j < r; j++) count[j] = 0; // Initialize count
// Count the number of records for each bin on this pass
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) count[(A[j]/rtok)%r]++;
// count[j] will be index in B for last slot of bin j.
// First, reduce count[0] because indexing starts at 0, not 1
count[0] = count[0] - 1;
for (j = 1; j < r; j++) count[j] = count[j-1] + count[j];
// Put records into bins, working from bottom of bin
// Since bins fill from bottom, j counts downwards
for (j = n-1; j >= 0; j--) {
B[count[(A[j]/rtok)%r]] = A[j];
count[(A[j]/rtok)%r] = count[(A[j]/rtok)%r] - 1;
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) A[j] = B[j]; // Copy B back
}
}
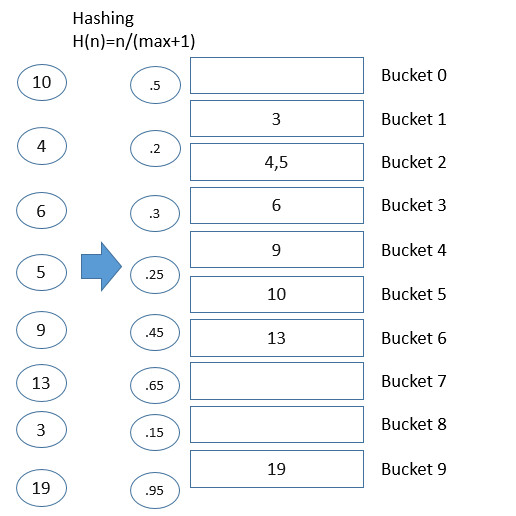
桶排序(bucket sort)
/**
* @param a 待排序数组元素
* @param step 步长(桶的宽度/区间),具体长度可根据情况设定
* @return 桶的位置/索引
*/
private int indexFor(int a,int step){
return a/step;
}
public void bucketSort(int []arr){
int max=arr[0],min=arr[0];
for (int a:arr) {
if (max<a)
max=a;
if (min>a)
min=a;
}
//该值也可根据实际情况选择
int bucketNum=max/10-min/10+1;
List buckList=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
//create bucket
for (int i=1;i<=bucketNum;i++){
buckList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//push into the bucket
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
int index=indexFor(arr[i],10);
((ArrayList<Integer>)buckList.get(index)).add(arr[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> bucket=null;
int index=0;
for (int i=0;i<bucketNum;i++){
bucket=(ArrayList<Integer>)buckList.get(i);
insertSort(bucket);
for (int k : bucket) {
arr[index++]=k;
}
}
}
//把桶内元素插入排序
private void insertSort(List<Integer> bucket){
for (int i=1;i<bucket.size();i++){
int temp=bucket.get(i);
int j=i-1;
for (; j>=0 && bucket.get(j)>temp;j--){
bucket.set(j+1,bucket.get(j));
}
bucket.set(j+1,temp);
}
}
排序後的搜尋
循序搜尋法(Linear Search)
import java.util.Scanner;
class LinearSearch
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int c, n, search, array[];
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number of elements");
n = in.nextInt();
array = new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter " + n + " integers");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
array[c] = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value to find");
search = in.nextInt();
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
if (array[c] == search) /* Searching element is present */
{
System.out.println(search + " is present at location " + (c + 1) + ".");
break;
}
}
if (c == n) /* Searching element is absent */
System.out.println(search + " is not present in array.");
}
}
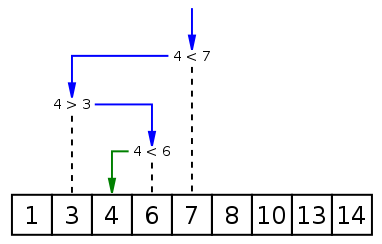
二分搜尋法(Binary Search)
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* The {@code BinarySearch} class provides a static method for binary
* searching for an integer in a sorted array of integers.
* <p>
* The <em>indexOf</em> operations takes logarithmic time in the worst case.
* <p>
* For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model">Section 1.1</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class BinarySearch {
/**
* This class should not be instantiated.
*/
private BinarySearch() { }
/**
* Returns the index of the specified key in the specified array.
*
* @param a the array of integers, must be sorted in ascending order
* @param key the search key
* @return index of key in array {@code a} if present; {@code -1} otherwise
*/
public static int indexOf(int[] a, int key) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = a.length - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
// Key is in a[lo..hi] or not present.
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
if (key < a[mid]) hi = mid - 1;
else if (key > a[mid]) lo = mid + 1;
else return mid;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the specified key in the specified array.
* This function is poorly named because it does not give the <em>rank</em>
* if the array has duplicate keys or if the key is not in the array.
*
* @param key the search key
* @param a the array of integers, must be sorted in ascending order
* @return index of key in array {@code a} if present; {@code -1} otherwise
* @deprecated Replaced by {@link #indexOf(int[], int)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public static int rank(int key, int[] a) {
return indexOf(a, key);
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of integers from the whitelist file, specified as
* a command-line argument; reads in integers from standard input;
* prints to standard output those integers that do <em>not</em> appear in the file.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// read the integers from a file
In in = new In(args[0]);
int[] whitelist = in.readAllInts();
// sort the array
Arrays.sort(whitelist);
// read integer key from standard input; print if not in whitelist
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int key = StdIn.readInt();
if (BinarySearch.indexOf(whitelist, key) == -1)
StdOut.println(key);
}
}
}